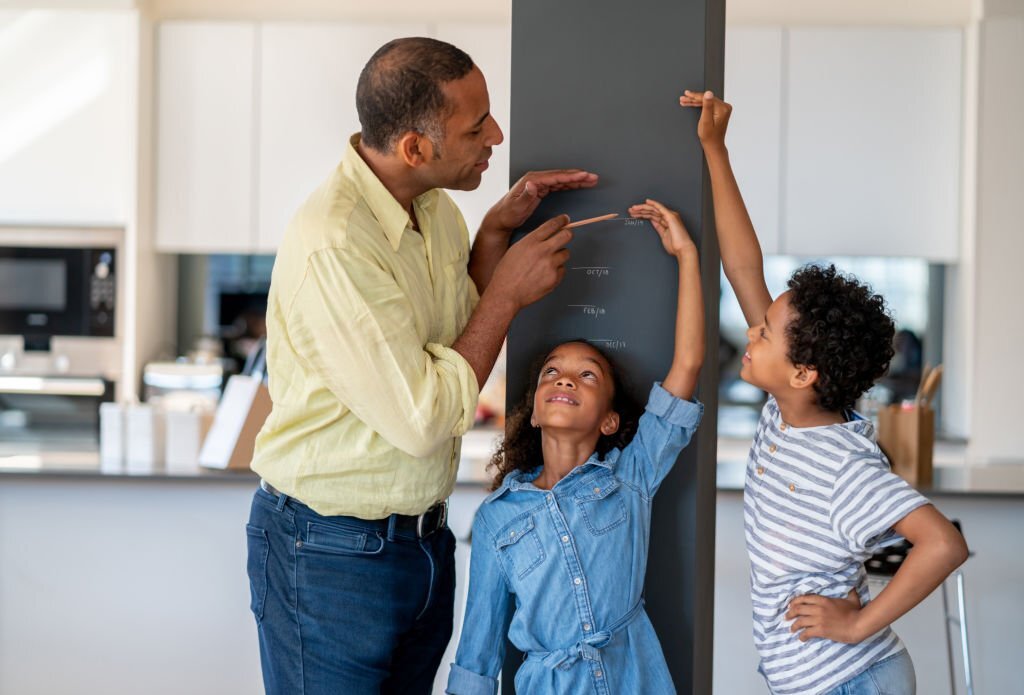
Growth hormones are one of those things we tend to take for granted. We don't think about it much unless something goes wrong. But there are actually many reasons why people seek out growth hormone treatments. One of the most common ones is to help someone with dwarfism reach their full potential.
Children born with dwarfism often suffer from poor bone health and low muscle mass, making it difficult for them to stand up straight. This makes it hard to participate in sports and other activities. With growth hormone treatment, patients start off small, then slowly gain weight and build muscle over time. As their bones strengthen, they'll eventually stop growing.
The body produces human growth hormone during puberty. After adolescence, our bodies naturally produce less and less of it. By adulthood, levels drop even lower.
For people with growth hormone deficiencies, this doesn't mean they won't ever grow tall again. Instead, they just won't grow as tall as they could. And because they lack adequate levels of growth hormone, their bones become weaker.
In addition to being unable to grow taller, adults who receive growth hormone treatments also face another problem: their skin becomes thinner and drier. Many doctors believe this is due to the fact that the hormone boosts metabolism, causing the body to burn calories faster. While this isn't necessarily bad, it can lead to dryness and wrinkles.
So if you've considered growth hormone treatments to boost your height, keep in mind that they don't provide the same benefits for adults as they do for kids.
How Does HGH Work to Increase Height?
Growth hormones are often thought of as a treatment option for kids with short stature. However, there are several things to know about how it works, what it does for adults, and whether it really makes any difference.
Growth hormone is made by the pituitary gland, located near the base of the brain. It controls the release of other hormones, including thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1).
When someone takes a growth hormone supplement, the body absorbs the hormone through the bloodstream. Once inside the cells, the hormone stimulates the liver to produce IGF-1.
The IGF-1 then travels to the rest of the body, where it helps promote healthy tissue growth.
The main effect of growth hormones is encouraging mass muscle growth. However, it also has a number of secondary benefits.
These include helping to build strong bones, improving metabolism, and reducing inflammation.
So, the idea behind growth hormone therapy is simple: it helps the body produce more of the hormone IGF-1, which stimulates bone growth and causes cells to divide faster.
This process happens naturally during puberty but stops once we reach adulthood. Doctors prescribe GH supplements orally or via injection for those who don't have enough natural production.
There are three types of growth hormones:
- recombinant human growth hormone (rHGH),
- somatropin, and
- biosynthetic human growth hormone (biohGH).
rHGH is derived from genetically engineered bacteria, while biohGH is produced in the gut of pigs. On the other hand, somatropin is extracted from the pituitary glands of cadavers.
While many people think that injecting themselves with growth hormones will give them extra inches, it won't necessarily work that way.
Most growth hormones stimulate cell division, but they don't actually affect our bones directly. They're more like a catalyst that speeds up the process of bone formation.
This means that growth hormone treatments may not make you taller right away. It's possible that after taking the drug for a few months, you might notice an increase in height. But most likely, you won't see much change at all.
So, Is HGH Effective at Increasing Adult Height?
Studies show that adult growth hormone therapies can be effective at increasing height by between 2 and 4 centimeters (cm) per year.
However, these studies were conducted on children, so it's unclear if the results would apply to adults. In addition, some experts say that the effects of growth hormone treatments aren't permanent.
At 20, your body produces less than half the amount of growth hormone that it did when you were younger. This means that even though you'll continue to grow throughout your life, you won't experience the same growth rate as you did when you were young.
In fact, one study found that men who took growth hormone injections for two years ended up growing only 0.5 cm longer than their non-treated counterparts.
If you want to increase your height permanently, you should consider a surgical procedure called epiphysiodesis. This involves cutting off the ends of one or both legs, so the bones stop growing.
It's a drastic measure, but it can help you achieve your dream of reaching your full potential.
HGH is usually used for adults to treat conditions such as dwarfism, Turner syndrome, and acromegaly. These conditions involve too little or too much growth hormone, respectively.
In addition, some researchers are investigating the use of growth hormones to combat obesity. The theory is that by boosting levels of IGF-1, the hormone could help the body burn fat more efficiently.
But despite its promise, there's no evidence yet that growth hormone injections can actually do this.
What Are the Risks of Taking Growth Hormones?
As mentioned above, growth hormone supplements have been around since the 1950s. And although they've been proven safe for children, their long-term safety remains unknown.
Some research suggests that growth hormone therapy may cause cancer. For example, a study published in 2009 found that patients who took growth hormones had higher rates of prostate cancer than those who didn't take the drugs.
Another concern is that growth hormone increases the risk of diabetes. A review published in 2010 suggested that people with type 1 diabetes are twice as likely to develop the condition when they take growth hormones.
And finally, some people worry about the possibility of developing gigantism. This occurs when someone becomes abnormally tall due to an overabundance of growth hormones.
Although rare, gigantism does occur naturally in humans. But most cases are caused by genetic disorders like Laron syndrome.
Laron syndrome is a disorder that causes people to grow unusually large muscles and bones. People with this condition tend to be extremely muscular and very tall.
However, even though growth hormone therapy may pose risks, many doctors believe it should still be available to people with certain medical problems.
One reason is that it can improve the quality of life. Another is because it can reduce pain and increase mobility.
If you're considering taking growth hormone, talk to your doctor first. They will be able to tell if you qualify for treatment based on your health history and current symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HGH has become increasingly popular over the past decade. While it's true that it doesn't actually increase height, it does help to stimulate growth hormone production in your body.
This means that it helps keep your muscles strong and lean, leading to increased muscle mass. In turn, this allows you to build more strength and endurance than ever before.
While it's true that HGH supplements aren't going to magically transform your body overnight, they can provide a boost that will allow you to achieve your fitness goals faster than ever before.
So whether you want to gain muscle mass or improve your cardiovascular system, HGH supplements can help you reach your goals sooner than you thought possible.